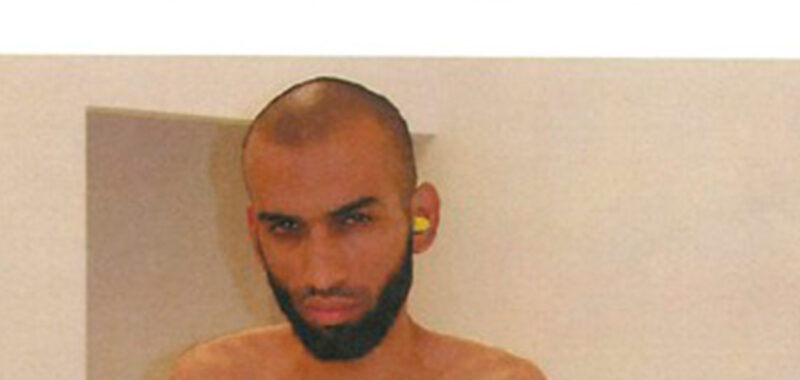
An emaciated man stands alone. He’s naked and in an all-too-white room. The hair on his head has recently been shaved, though his beard is full. The handcuffs shackling his wrists appear oversized for his small frame. A yellow earplug is jammed in only one ear.
This photograph is the public’s first, and so far only, look at a War on Terror detainee in a Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) black site: a secret detention center set up to hold and interrogate prisoners who have not been charged with a crime. It’s a surprising image, stark and overexposed, both in terms of how bright the photograph is and how naked the man is. Someone employed by the CIA took this photograph, though we don’t know who. But we do know why it was taken, and who it is in the frame.
His name is Ammar al-Baluchi, a detainee at Guantanamo Bay currently facing capital charges for the 9/11 attacks. This photograph, likely from 2004, is from the period before he was transported to the United States’s offshore penal colony in 2006. Baluchi was one of at least 119 Muslim men held incommunicado by the CIA for years in its global network of clandestine black sites, where he and at least 38 others were repeatedly subject to “enhanced interrogation techniques,” a US-government euphemism for torture.
From May 2003 to September 2006, Baluchi was secretly shuffled between five black sites, including one in Romania, where this photo is believed to have been taken. (The photo, recently declassified, was provided to me by Baluchi’s lawyers, who added the black band across his midsection to preserve his dignity. I broke the story surrounding the photograph and Baluchi for the Guardian earlier this year.) Whenever any of these Muslim men were moved, CIA protocol dictated that field officers photograph each one, both naked and clothed, “to document his physical condition at the time of transfer.”
The image before us isn’t just any photograph. It’s visual evidence of crimes authorized and committed by the United States government, an entry in the annals of self-reported atrocity photography. In all, the CIA took some 14,000 photographs of the agency’s black sites around the world, but we, the public, have never been able to see any of them until now.
There are plenty of examples of this macabre genre. Israel produces it. So does Syria’s Bashar al-Assad. As did the Khmer Rouge in Cambodia. The Nazis. The Soviets. The French. Governments of different political leanings have contributed to this dark archive, uniting the magical technology of the camera with the awesome power of detention and even death. They take pictures of their own crimes and immediately file them away, in an acrobatic technocratic act of simultaneous remembering and forgetting.
The question is why. A photograph, presumably, is meant to be seen. These images, on the other hand, were intended to record but almost never to be viewed. They were certainly never meant to be seen by the public.
Of course, anyone who has used their phone camera to take a picture of a receipt knows that a photograph doesn’t have only a public function. It can also operate as a trace of memory and documentation of a transaction. Self-reported atrocity photographs, indeed, fulfill the record-keeping needs of a government bureaucracy. The fact that the CIA was using black sites was revealed to the public in 2005, but it was not until 2015 that the photo archive documenting them was exposed. In response to that revelation, a US government official described the photographs as having been “taken for budgetary reasons to document how money was being spent.” Behold the banality of bureaucratic evil.

Photography, since its inception, has subjected Muslim men to coercive violence. In 1850, barely a decade after the invention of photography in 1839, French travel writer Maxime Du Camp sojourned with the novelist Gustave Flaubert through Egypt, Nubia, Palestine, and Syria, taking pictures along the way. On the Nile, Du Camp routinely photographed one of the sailors on his steamer, Hajj Ishmael, usually with the latter draped in just a loin cloth. “He was an extremely handsome Nubian,” Du Camp writes in his travelogue. “I sent him climbing up onto the ruins which I wanted to photograph, and that way, I was able to obtain an exact scale of proportions.”
The challenge in early photography, with its long exposure times, was to get your subjects to sit still. Du Camp came up with a solution that he proudly described to his friend, the French poet Théophile Gautier. “I finally arrived at the idea of a rather baroque deception that will make you, dear Théophile, understand something about the gullible naiveté of these poor Arabs,” he wrote. “I told him that the copper pipe of my lens jutting out of the camera was a cannon that would burst into shrapnel if he had the misfortune to move while I was pointing it in his direction, a story which immobilized him completely. Persuaded, Hajj Ishmael did not move for more than a minute.”
I suppose there’s a reason why we talk about a “photo shoot.”
“To photograph people is to violate them,” Susan Sontag writes in On Photography (1977), “by seeing them as they never see themselves, by having knowledge of them they can never have; it turns people into objects that can be symbolically possessed. Just as the camera is a sublimation of the gun, to photograph someone is sublimated murder — a soft murder, appropriate to a sad, frightened time.”

More than any other subgenre, it is self-reported atrocity photography that most closely approximates the murder Sontag describes. During the first two years of Bashar al-Assad’s violent repression of a popular uprising in Syria, a photographer who worked for the military police was assigned the duty of taking pictures of the corpses of civilians the regime killed. The bodies were mostly in military hospitals, often in a severely mutilated state. Initially, each corpse had the person’s name written on it. Eventually, names were replaced with three sets of numbers, the first indicating who the person was, the second pointing to the branch of the intelligence service responsible for the imprisonment, and the third referring to the person’s medical report, stripping them of the final remnants of their humanity.
It became immediately clear to the photographer, who is now known by the pseudonym “Caesar,” that these people were being tortured to death. Government higher-ups required his photos as proof that their orders to punish and kill dissidents were being carried out. For two years, he did his work while smuggling copies of over 52,000 of those photos out of the country, before defecting in 2013. His photos have since been displayed around Europe and North America and have been instrumental in proving Assad’s ruthlessness.
In Caesar’s photographs, mostly captured with a Nikon Coolpix P50, the people photographed are already dead. The camera operates as an apparatus of confirmation, the final stage of the government’s killing machine.
The Khmer Rouge also systematically documented the atrocities they committed. More than a fifth of the Cambodian population died during its genocidal rule between 1975 and 1979. The Khmer Rouge’s most notorious political prison and torture center Tuol Sleng, also known as S-21, was a converted high school in the middle of Phnom Penh, through which more than 14,000 people were shuttled. Fewer than a dozen survived. Each person was photographed upon entry, many by Nhem En, S-21’s chief photographer, who was only 15 years old when the Khmer Rouge sent him to China to study photography. He returned six months later with a Chinese box camera and began working at S-21.

What we see in the photographs of S-21 is the sober reality that those brought and photographed here are marked for death, even though, unlike Caesar’s photos, they are still alive when photographed. By capturing the imminence of their demise, the photographer closes in on killing them, not by knife or bullet but by immortalizing them. Death pervades the frame of the living, which makes a photo of Kong Saman, for example, all the more stunning. A child’s tiny, bony arm and hand extend upward, grabbing the woman’s sleeve. We can’t see the child’s face, but the gesture is enough to remind us of the horrifying fact that young life coexists with mechanized death.
In both the Syrian and Khmer Rouge examples, the photographers themselves have been identified. That knowledge, along with the change of venue (from hidden government files to art museum or US Congress) and the political purpose of their display, which serves to prove the brutality of the exhibiting state’s enemies, has radically changed our perception and reception of these images. What was once meant as evidence of efficiency has transformed into proof of brutality. If the photographs previously functioned to label enemies who had been exterminated, they now serve as mementos to identify and remember specific victims.
The Tuol Sleng photographs gained particular fame after a 1997 exhibition at New York’s Museum of Modern Art featuring about 20 images from the archive. The Caesar photos have been exhibited widely, from the United States Holocaust Memorial Museum to the European Union Parliament and beyond. But exhibiting the photos in a museum or public hall desensitizes the viewer by making the images feel as if they are fully understood objects, either as historical artifacts or works of art, quite unlike the Baluchi photograph, which remains opaque.
None of this extra knowledge is brought to this now 20-year-old photograph of Ammar al-Baluchi. We don’t know who took the picture, and it hasn’t been exhibited in any galleries or political halls of power. All we know is that this is but one of 14,000 photos, that Baluchi was tortured by the CIA, and that no one in the US government has ever been held accountable for the torture program it put into place following the 9/11 attacks.
Self-reported atrocity photography, however, transcends government bureaucracy, in the same way that photography is more than simply a visual record. Like all images of its kind, the Baluchi photo records a massive imbalance of power: He is naked before the photographer’s lens and helpless before the machine of the state. Despite this disparity, Baluchi looks straight through the lens with a defiant, wounded, and all-too-human expression. With that gaze, he manages to resist his own soft murder. Despite his shrunken size and condition, he fills the photograph with life and presence. While his body appears defeated, his face looks ready to free himself of the photograph by force of will alone. And that may be the greatest surprise of all. The irony behind this image is that, while it is Baluchi in the frame, it is the nameless photographer, and the apparatus of power behind him, who remain in hiding.